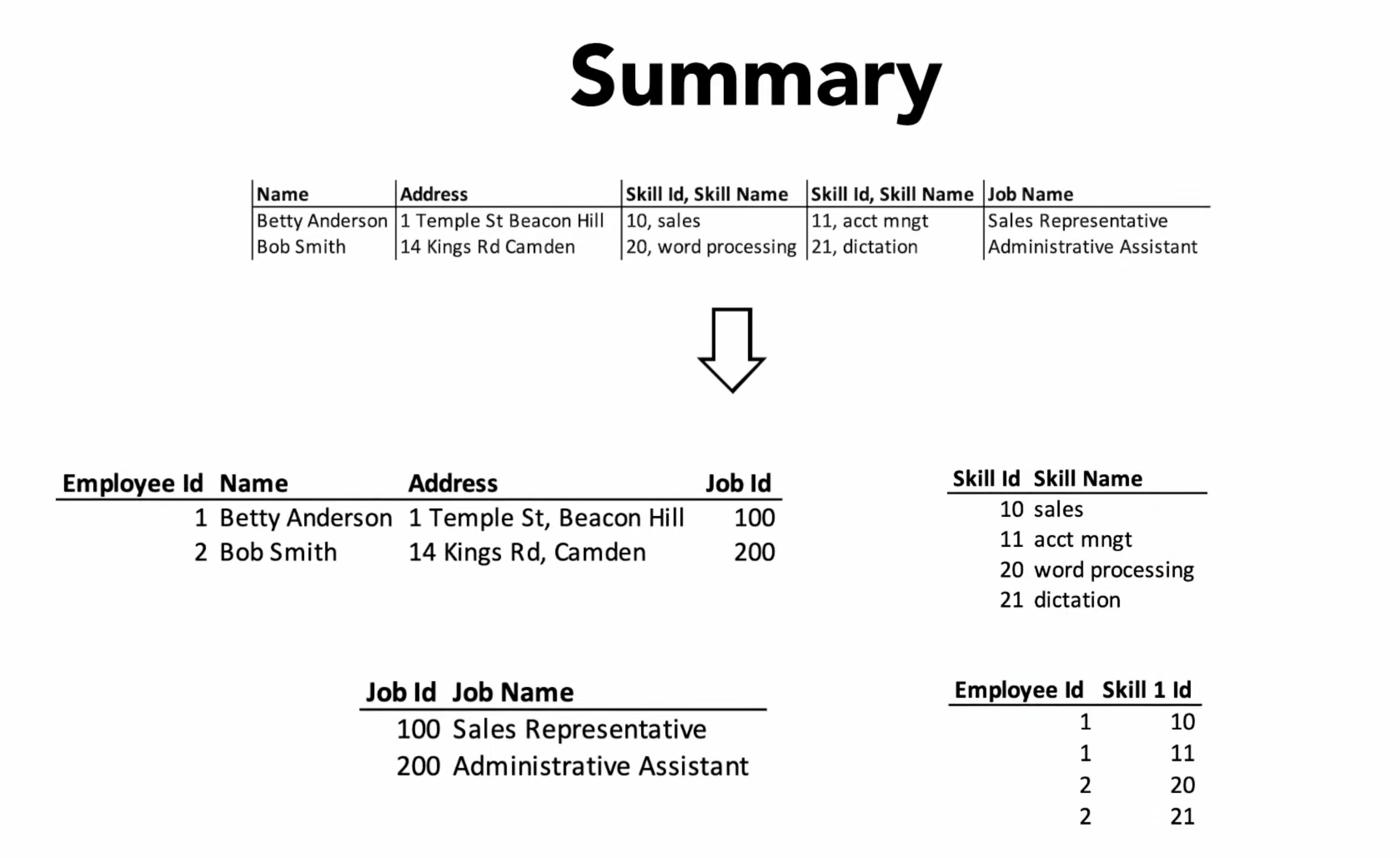
4.1. Normalization About¶
Entities - rows in database
Attributes - columns in database
Normalization is what gives data meaning
NF - Normal Form
In order to be in 3rd normal form, you need to be in 1st and 2nd NF
Core basics: 1st, 2nd, 3rd
Exceptions: 4th, 5th
1st: atomic values, unique identifiers (PK), columns with same type
2nd: all data must depend on the Primary Key
3rd: PK define all Non-Key columns, those can't depend on any other Key
4th: No multi-valued dependencies
4.1.1. Normal forms¶
UNF: Unnormalized form
1NF: First normal form
2NF: Second normal form
3NF: Third normal form
EKNF: Elementary key normal form
BCNF: Boyce–Codd normal form
4NF: Fourth normal form
ETNF: Essential tuple normal form
5NF: Fifth normal form
DKNF: Domain-key normal form
6NF: Sixth normal form
4.1.2. Glossary¶
- normalization¶
Database normalization is the process of structuring a database, usually a relational database, in accordance with a series of so-called normal forms in order to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity. Normalization entails organizing the columns (attributes) and tables (relations) of a database to ensure that their dependencies are properly enforced by database integrity constraints. It is accomplished by applying some formal rules either by a process of synthesis (creating a new database design) or decomposition (improving an existing database design). A relational database relation is often described as 'normalized' if it meets third normal form. [1] [2]
- NF¶
Normal Form
- Entity¶
- Entities¶
Rows in database
- Attributes¶
Columns in database
- Table¶
Database Table
4.1.3. Recap¶