6.15. Idiom Patterns¶
Python
forloop is equivalent toforEachin other languagesOther languages
forloop is Python'swhile(sic!)
For:
for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) # C/C++/Java for (var i = 0; i <= 10; i++) # JavaScript i = 0 while i <= 10: # Python i += 1
ForEach Index:
for (let idx in collection) # JavaScript for idx in range(len(collection)) # Python
ForEach Element:
for (var element : collection) # Java for (let element of collection) # JavaScript for element in collection # Python for i in range(0,10) # Python
Enumerate:
for (int i = 0; i <= collection.length; i++) # C++ / JAVA / JavaScript element = collection[i] for (let i in collection) # JavaScript element = collection[i] for i in range(len(collection)): # Python (1to1 algorithm conversion) element = collection[i] for i, element in enumerate(collection) # Python (Pythonic way)
Zip:
for (int i = 0; i <= collection.length; i++) # C++ / JAVA / JavaScript a = collection1[i] b = collection2[i] for i in range(len(collection1)): # Python (1to1 algorithm conversion) a = collection1[i] b = collection2[i] for a, b in zip(collection1, collection2) # Python (Pythonic way)
Code Complexity vs. Programmer Experience:
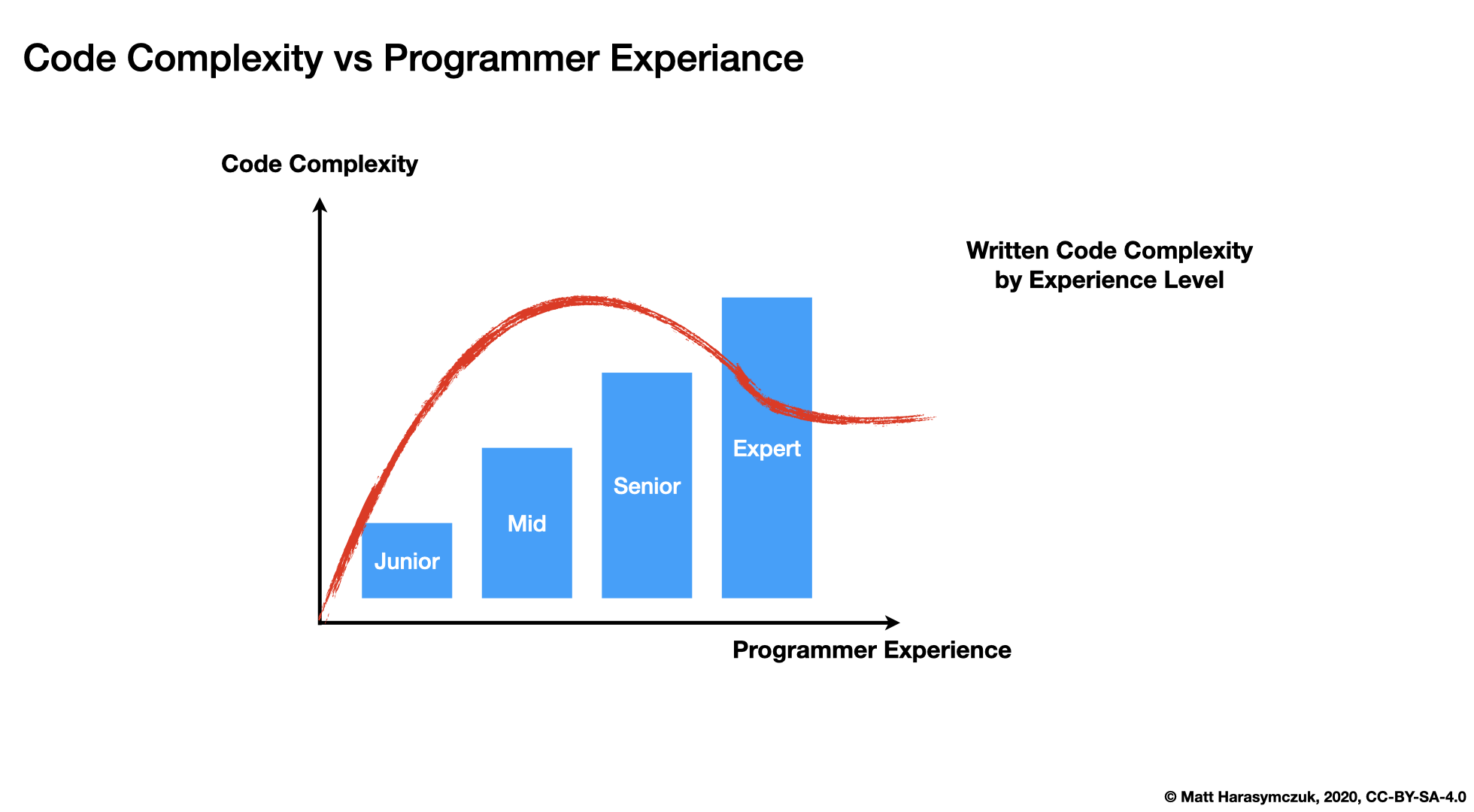
Time Complexity: https://wiki.python.org/moin/TimeComplexity
6.15.1. Loop Patterns¶
>>> data = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> i = 0
>>> result = []
>>>
>>> while i < len(data):
... x = data[i]
... result.append(x.upper())
... i += 1
>>>
>>> print(result)
['A', 'B', 'C']
>>> data = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> result = []
>>>
>>> for x in data:
... result.append(x.upper())
>>>
>>> print(result)
['A', 'B', 'C']
>>> data = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> result = [x.upper() for x in data]
>>>
>>> print(result)
['A', 'B', 'C']
6.15.2. Range¶
>>> i = 0
>>>
>>> while i < 5:
... i += 1
>>> for i in range(5):
... pass
6.15.3. ForEach¶
>>> DATA = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>>
>>> for i in range(len(DATA)):
... value = DATA[i]
>>> DATA = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>>
>>> for value in DATA:
... pass
6.15.4. Sum¶
>>> DATA = [1, 2, 3]
>>> result = 0
>>>
>>> for i in range(len(DATA)):
... result += DATA[i]
>>> DATA = [1, 2, 3]
>>> result = sum(DATA)
6.15.5. Enumerate¶
>>> DATA = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> i = 0
>>>
>>> while i < len(DATA):
... value = DATA[i]
... i += 1
>>> DATA = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>>
>>> for i, value in enumerate(DATA):
... pass
6.15.6. Zip¶
>>> header = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> values = [1, 2, 3]
>>> result = {}
>>>
>>> for i in range(len(header)):
... key = header[i]
... val = values[i]
... result[key] = value
>>> header = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> values = [1, 2, 3]
>>>
>>> result = zip(header, values)
>>> dict(result)
{'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
6.15.7. List Comprehension¶
>>> DATA = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> result = []
>>>
>>> for x in DATA:
... result.append(x)
...
>>> result
['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> DATA = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>>
>>> result = [x for x in DATA]
>>> result
['a', 'b', 'c']
6.15.8. Set Comprehension¶
>>> DATA = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> result = set()
>>>
>>> for x in DATA:
... result.add(x)
>>> DATA = ['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> result = {x for x in DATA}
6.15.9. Dict Comprehension¶
>>> DATA = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
>>> result = dict()
>>>
>>> for key, value in DATA.items():
... result[key] = value
>>> DATA = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}
>>> result = {k:v for k,v in DATA.items()}
6.15.10. Map¶
>>> def func(x):
... return float()
...
>>> DATA = [1, 2, 3]
>>> result = (func(x) for x in DATA)
>>> def func(x):
... return float()
...
>>> DATA = [1, 2, 3]
>>> result = map(func, DATA)
6.15.11. Filter¶
>>> def func(x):
... return x % 2 == 0
...
>>> DATA = [1, 2, 3]
>>> result = (x for x in DATA if func(x))
>>> def func(x):
... return x % 2 == 0
...
>>> DATA = [1, 2, 3]
>>> result = filter(func, DATA)
6.15.12. For Else¶
>>> DATA = [1, 2, 3]
>>> FIND = 10
>>> found = False
>>>
>>> for value in DATA:
... if value == FIND:
... print('Found')
... found = True
... break
...
>>> if not found:
... print('Not Found')
Not Found
>>> DATA = [1, 2, 3]
>>> FIND = 10
>>>
>>> for value in DATA:
... if value == FIND:
... print('Found')
... break
... else:
... print('Not Found')
Not Found
6.15.13. While Else¶
>>> DATA = [1, 2, 3]
>>> FIND = 10
>>> found = False
>>>
>>> while i < len(DATA):
... value = DATA[i]
... i += 1
... if value == FIND:
... print('Found')
... found = True
... break
...
>>> if not found:
... print('Not Found')
Not Found
>>> DATA = [1, 2, 3]
>>> FIND = 10
>>>
>>> while i < len(DATA):
... value = DATA[i]
... i += 1
... if value == FIND:
... print('Found')
... break
... else:
... print('Not Found')
Not Found
6.15.14. Str Startswith¶
>>> data = 'virginica'
>>> data[:1] == 'v'
True
>>> data[:3] == 'vir' or data[:2] == 've'
True
>>> data = 'virginica'
>>> data.startswith('v')
True
>>> data.startswith(('vir', 've'))
True
6.15.15. Str Endswith¶
>>> data = 'virginica'
>>> data[-3:] == 'osa'
False
>>> data[-3:] == 'osa' or data[-2:] == 'ca'
True
>>> data = 'setosa'
>>> data.endswith('osa')
True
>>> data.endswith(('osa', 'ca'))
True
6.15.16. Str Join Newline¶
>>> data = ['line1', 'line2', 'line3']
>>> result = [line+'\n' for line in data]
>>> data = ['line1', 'line2', 'line3']
>>> result = '\n'.join(data)
6.15.17. Others¶
all()any()iter()next()
6.15.18. Functools¶
from functools import *functools.reduce(function, iterable[, initializer])
6.15.19. Itertools¶
More information in Itertools
itertools.from itertools import *itertools.count(start=0, step=1)itertools.cycle(iterable)itertools.repeat(object[, times])itertools.accumulate(iterable[, func, *, initial=None])itertools.chain(*iterables)itertools.compress(data, selectors)itertools.islice(iterable, start, stop[, step])itertools.starmap(function, iterable)itertools.product(*iterables, repeat=1)itertools.permutations(iterable, r=None)itertools.combinations(iterable, r)itertools.combinations_with_replacement(iterable, r)itertools.groupby(iterable, key=None)